Open Theism Open Theism is the thesis that, because God loves us and desires that we freely choose to reciprocate His love, He has made His knowledge of, and plans for, the future conditional upon…
Catégorie de navigationWiki Philosophie
Emmanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant At the foundation of Kant’s system is the doctrine of “transcendental idealism,” which emphasizes a distinction between what we can experience (the natural, observable world) and what we cannot (“supersensible” objects such as…
Philosophy of Law
Philosophy of Law Philosophy of law (or legal philosophy) is concerned with providing a general philosophical analysis of law and legal institutions. Issues in the field range from abstract conceptual questions about the nature of…
Enfer
L'enfer en philosophie et en théologie, le mot "enfer,» dans son sens le plus général, fait référence à une sorte de mauvais état post-mortem. Le mot anglais est apparemment dérivé d'un mot indo-européen signifiant « couvrir »,” which…
Aristippus (c. 435—356 B.C.E.)
Aristippus (c. 435—356 B.C.E.) Aristippus was a follower of Socrates, and the founder of the Cyrenaic school of philosophy. Like other Greek ethical thinkers, Aristippus’ ethics are centered around the question of what the ‘end’ is;…
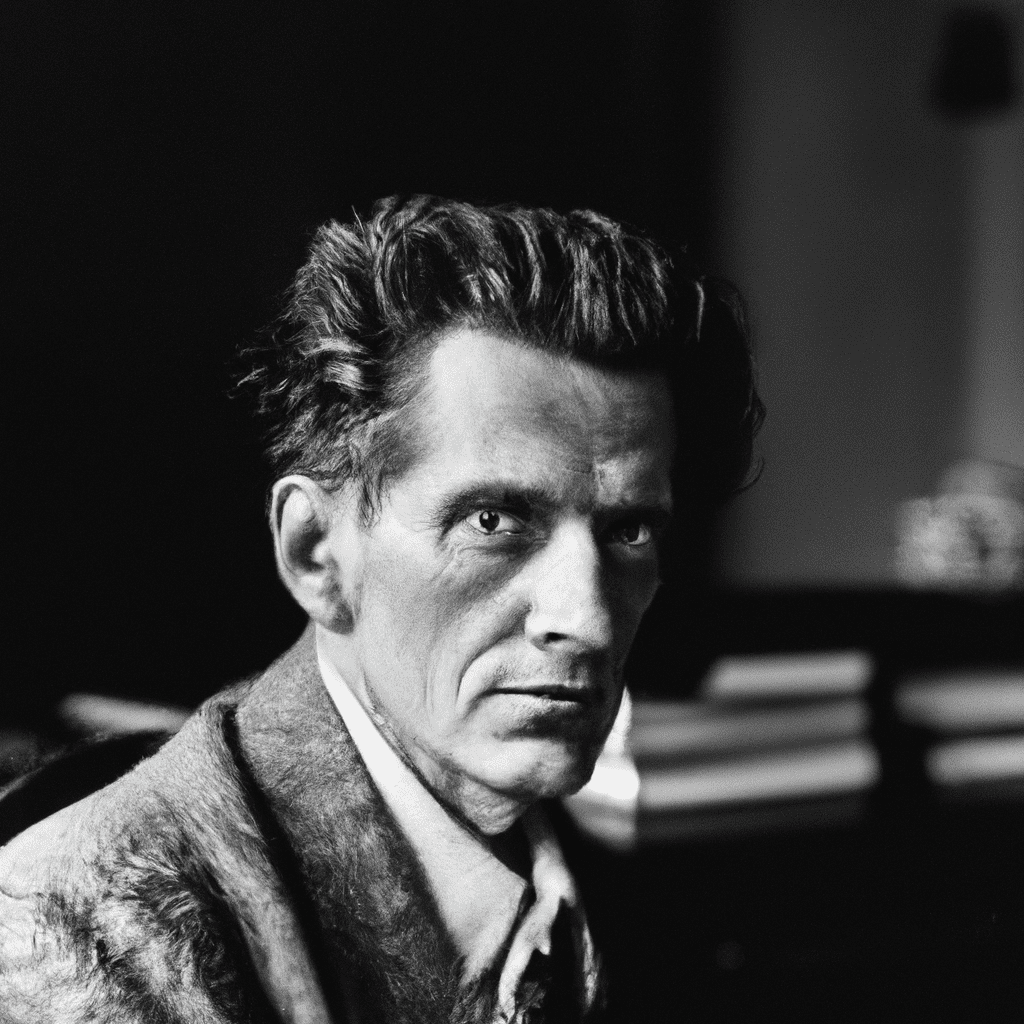
Louis Wittgenstein (1889—1951)
Louis Wittgenstein (1889—1951) Ludwig Wittgenstein is one of the most influential philosophers of the twentieth century, and regarded by some as the most important since Immanuel Kant. His early work was influenced by that of…
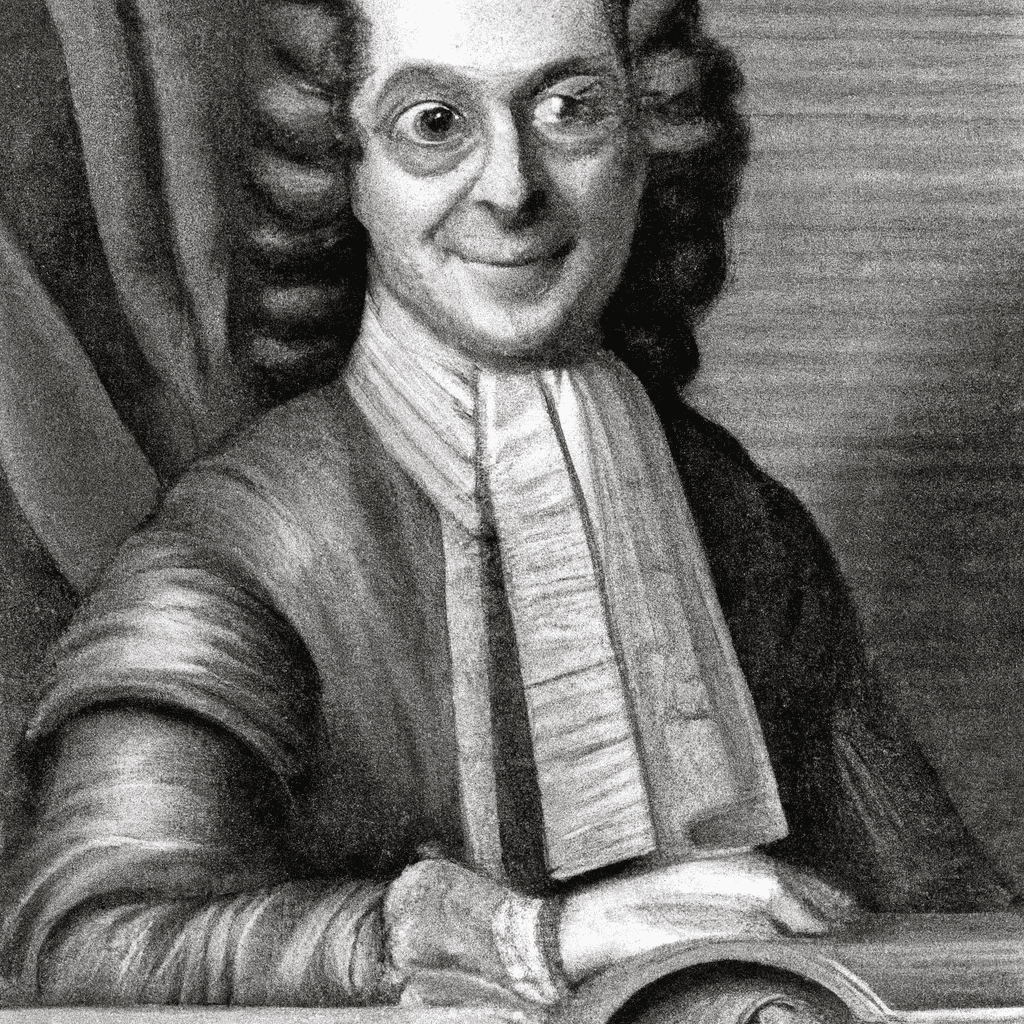
Bernard Mandeville (1670—1733)
Bernard Mandeville (1670—1733) Bernard Mandeville is primarily remembered for his impact on discussions of morality and economic theory in the early eighteenth century. His most noteworthy and notorious work is The Fable of the Bees,…
Introspection
Introspection Introspection is the process by which someone comes to form beliefs about her own mental states. We might form the belief that someone else is happy on the basis of perception – for example,…
Aristote: Motion
Aristote: Motion Aristotle’s account of motion and its place in nature can be found in the Physics. By motion, Aristote (384-322 avant notre ère) understands any kind of change. He defines motion as the actuality of a potentiality. Initialement,…
Bernard Bolzano: Philosophy of Mathematical Knowledge
Bernard Bolzano: Philosophy of Mathematical Knowledge In Bernard Bolzano’s theory of mathematical knowledge, properties such as analyticity and logical consequence are defined on the basis of a substitutional procedure that comes with a conception of…