Guo Xiang (c. 252—312 C.E.) Guo Xiang (also known as Kuo Hsiang and Zixuan) is the author of the most important commentary on the classic Daoist text Zhuangzi (Chuang-tzu). He is responsible for the current…
Browsing CategoryWiki Filosofía
Connectionism
Connectionism Connectionism is an approach to the study of human cognition that utilizes mathematical models, known as connectionist networks or artificial neural networks. Often, these come in the form of highly interconnected, neuron-like processing units….
Doxastic Conservatism
Doxastic Conservatism We are creatures with clear cognitive limitations. Our memories are finite and there is a limit to the kinds of things we can store and retrieve. We cannot, for example, remember the justification…
Augustine: Political and Social Philosophy
Augustine: Political and Social Philosophy St. Augustine (354-430 C.E.), originally named Aurelius Augustinus, was the Catholic bishop of Hippo in northern Africa. He was a skilled Roman-trained rhetorician, a prolific writer (who produced more than…
Epictetus (55–135 C.E.)
Epictetus (55–135 C.E.) Epictetus (pronounced Epic-TEE-tus) was an exponent of Stoicism who flourished in the early second century C.E. about four hundred years after the Stoic school of Zeno of Citium was established in Athens….
The Problem of the Criterion
The Problem of the Criterion The Problem of the Criterion is considered by many to be a fundamental problem of epistemology. In fact, Chisholm (1973, 1) claims that the Problem of the Criterion is “one…
Jerry A. Fodor (1935—2017)
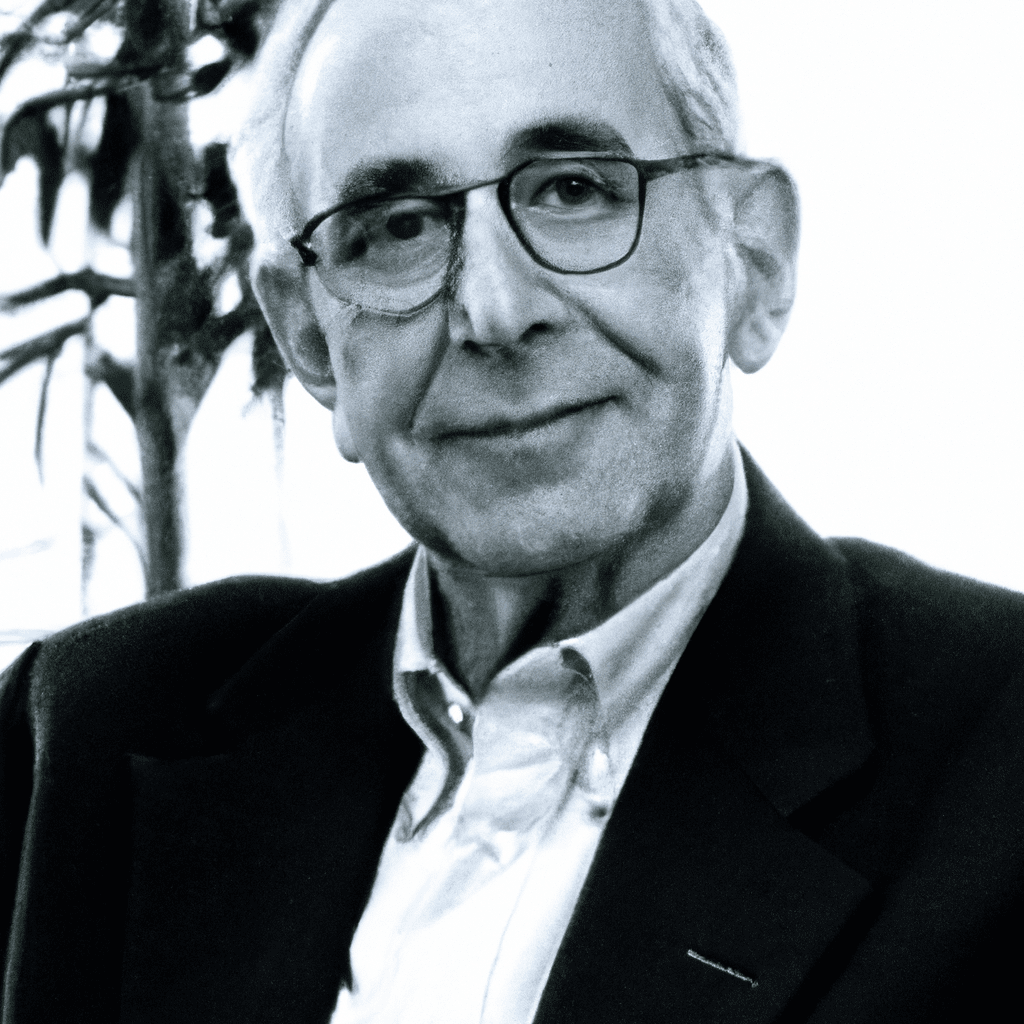
Jerry A. Fodor (1935—2017) Jerry Fodor was one of the most important philosophers of mind of the late twentieth and early twenty-first centuries. In addition to exerting an enormous influence on virtually all parts of…
Mind and the Causal Exclusion Problem
Mind and the Causal Exclusion Problem The causal exclusion problem is an objection to nonreductive physicalist models of mental causation. Mental causation occurs when behavioural effects have mental causes: Jennie eats a peach because she…
Epiphenomenalism
Epiphenomenalism Epiphenomenalism is a position in the philosophy of mind according to which mental states or events are caused by physical states or events in the brain but do not themselves cause anything. It seems…
Thick Concepts
Thick Concepts A term expresses a thick concept if it expresses a specific evaluative concept that is also substantially descriptive. It is a matter of debate how this rough account should be unpacked, but examples…