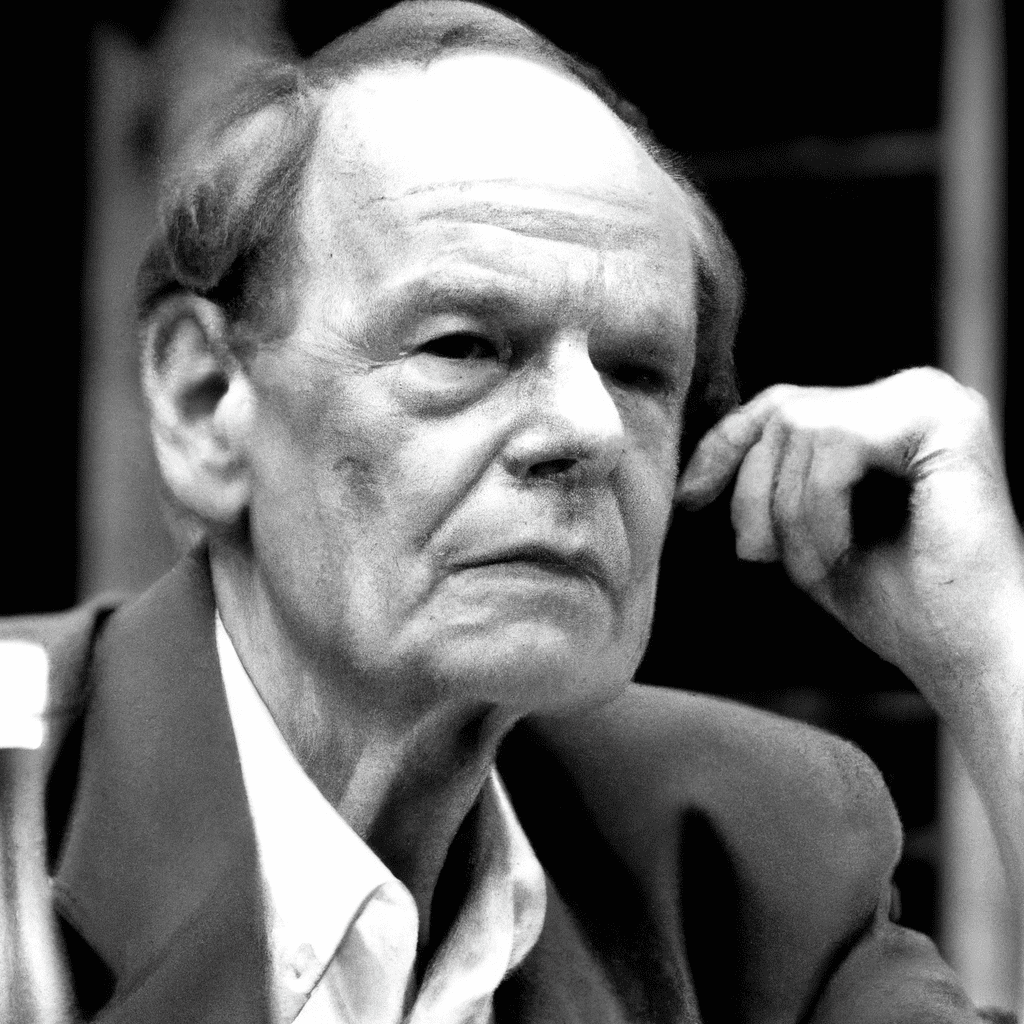
Gilles Deleuze (1925–1995) Deleuze is a key figure in postmodern French philosophy. Considering himself an empiricist and a vitalist, his body of work, which rests upon concepts such as multiplicity, constructivism, difference, and desire, stands…
Browsing CategoryWiki Filosofía
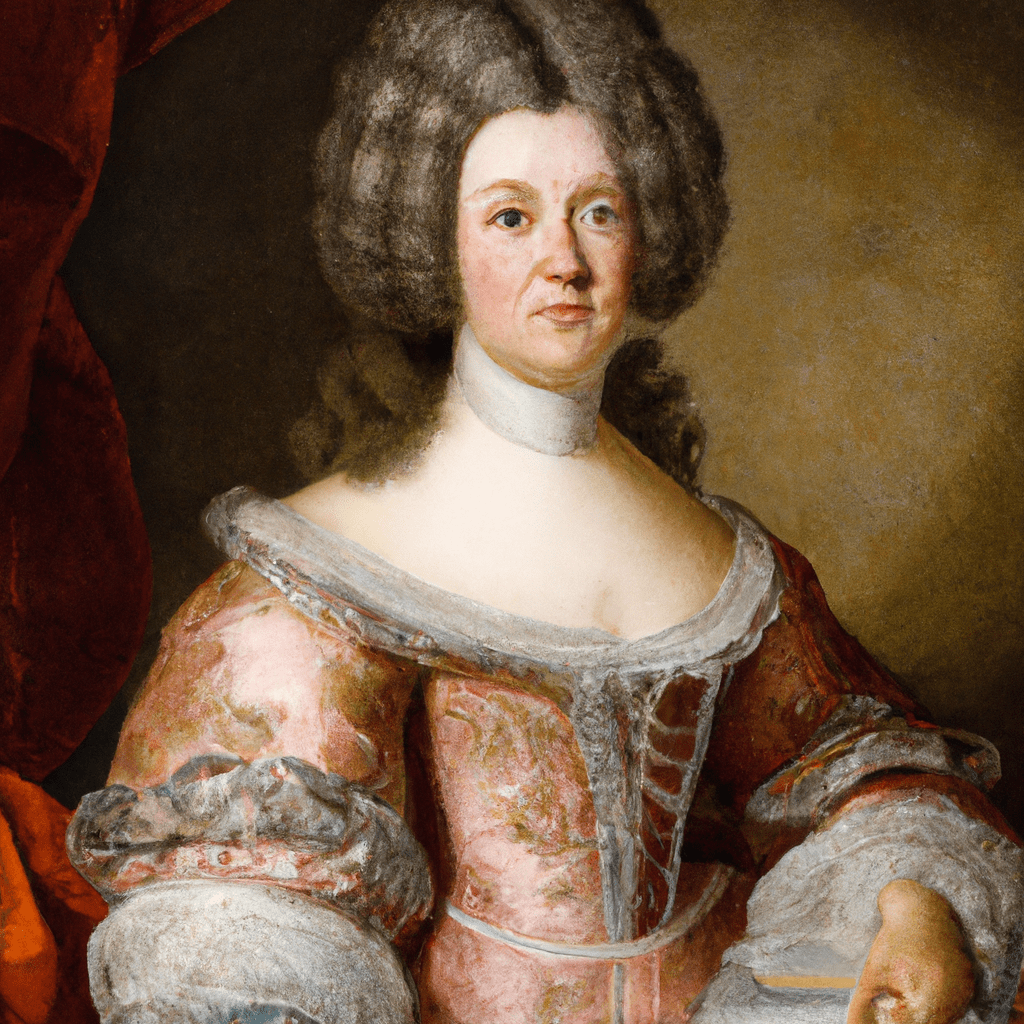
Anne-Thérèse Marguenat de Courcelles, marquise de Lambert (1647—1733)
Anne-Thérèse Marguenat de Courcelles, marquise de Lambert (1647—1733) A prominent salonnière in the France of Louis XIV and the Regency, Madame de Lambert authored numerous essays dealing with philosophical issues. Her most famous works, twin sets of…
Associationism in the Philosophy of Mind
Associationism in the Philosophy of Mind Association dominated theorizing about the mind in the English-speaking world from the early eighteenth century through the mid-twentieth and remained an important concept into the twenty-first. This endurance across…
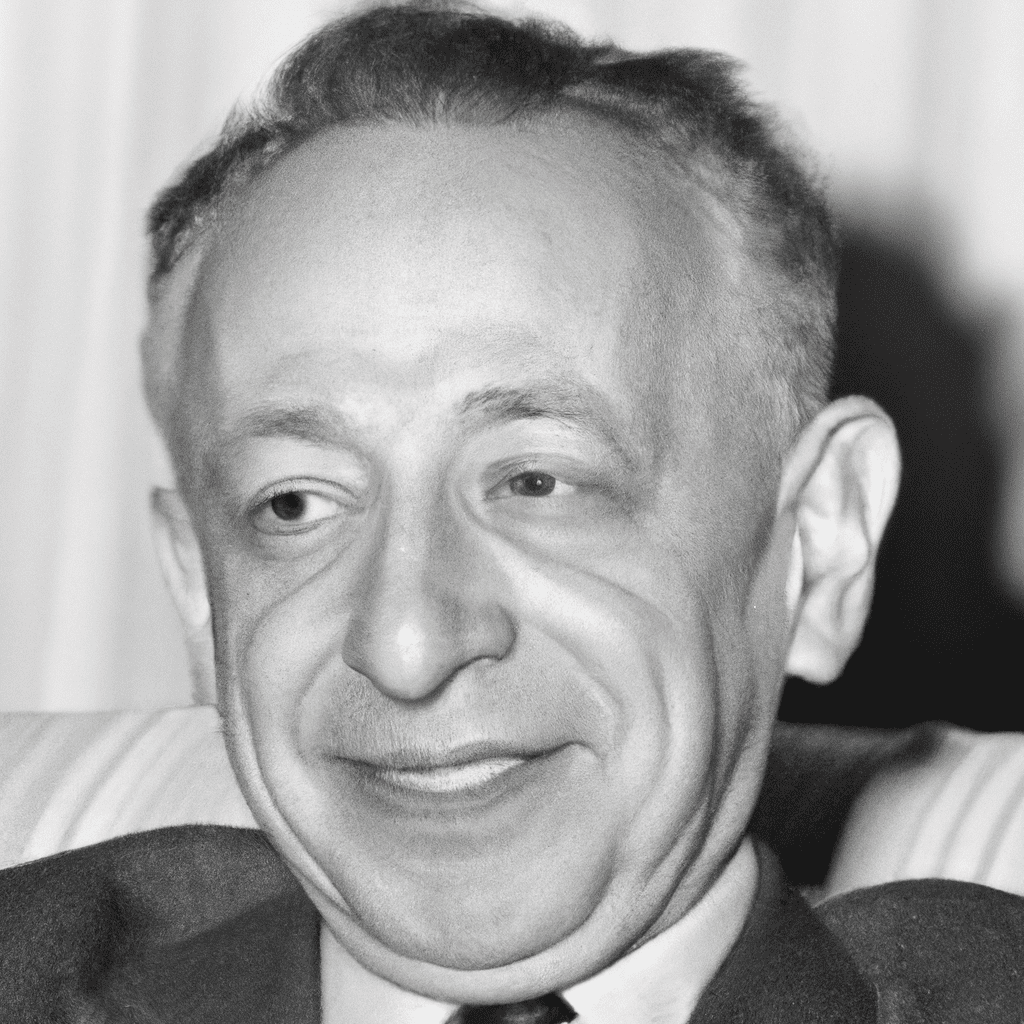
Cornelius Castoriadis (1922—1997)
Cornelius Castoriadis (1922—1997) Cornelius Castoriadis was an important intellectual figure in France for many decades, beginning in the late-1940s. Trained in philosophy, Castoriadis also worked as a practicing economist and psychologist while authoring over twenty…
Jeremy Bentham (1748—1832)
Jeremy Bentham (1748—1832) Jeremy Bentham was an English philosopher and political radical. He is primarily known today for his moral philosophy, especially his principle of utilitarianism, which evaluates actions based upon their consequences. The relevant…
Deductive-Theoretic Conceptions of Logical Consequence
Deductive-Theoretic Conceptions of Logical Consequence According to the deductive-theoretic conception of logical consequence, a sentence X is a logical consequence of a set K of sentences if and only if X is a deductive consequence…
Maimonides (1138—1204)
Maimonides (1138—1204) Maimonides is a medieval Jewish philosopher with considerable influence on Jewish thought, and on philosophy in general. Maimonides also was an important codifier of Jewish law. His views and writings hold a prominent…
Comparative Philosophy
Comparative Philosophy Comparative philosophy—sometimes called “cross-cultural philosophy”—is a subfield of philosophy in which philosophers work on problems by intentionally setting into dialogue various sources from across cultural, linguistic, and philosophical streams. The ambition and challenge…
Metaphysics of Science
Metaphysics of Science Metaphysics of Science is the philosophical study of key concepts that figure prominently in science and that, prima facie, stand in need of clarification. It is also concerned with the phenomena that…
Ancient Aesthetics
Ancient Aesthetics It could be argued that ‘ancient aesthetics’ is an anachronistic term, since aesthetics as a discipline originated in 18th century Germany. Nevertheless, there is considerable evidence that ancient Greek and Roman philosophers discussed…