Pragmatism Pragmatism is a philosophical movement that includes those who claim that an ideology or proposition is true if it works satisfactorily, that the meaning of a proposition is to be found in the practical…
Browsing CategoryWiki Filosofía
Thomas Aquinas (1224/6—1274)
Thomas Aquinas (1224/6—1274) St. Thomas Aquinas was a Dominican priest and Scriptural theologian. He took seriously the medieval maxim that “grace perfects and builds on nature; it does not set it aside or destroy it.”…
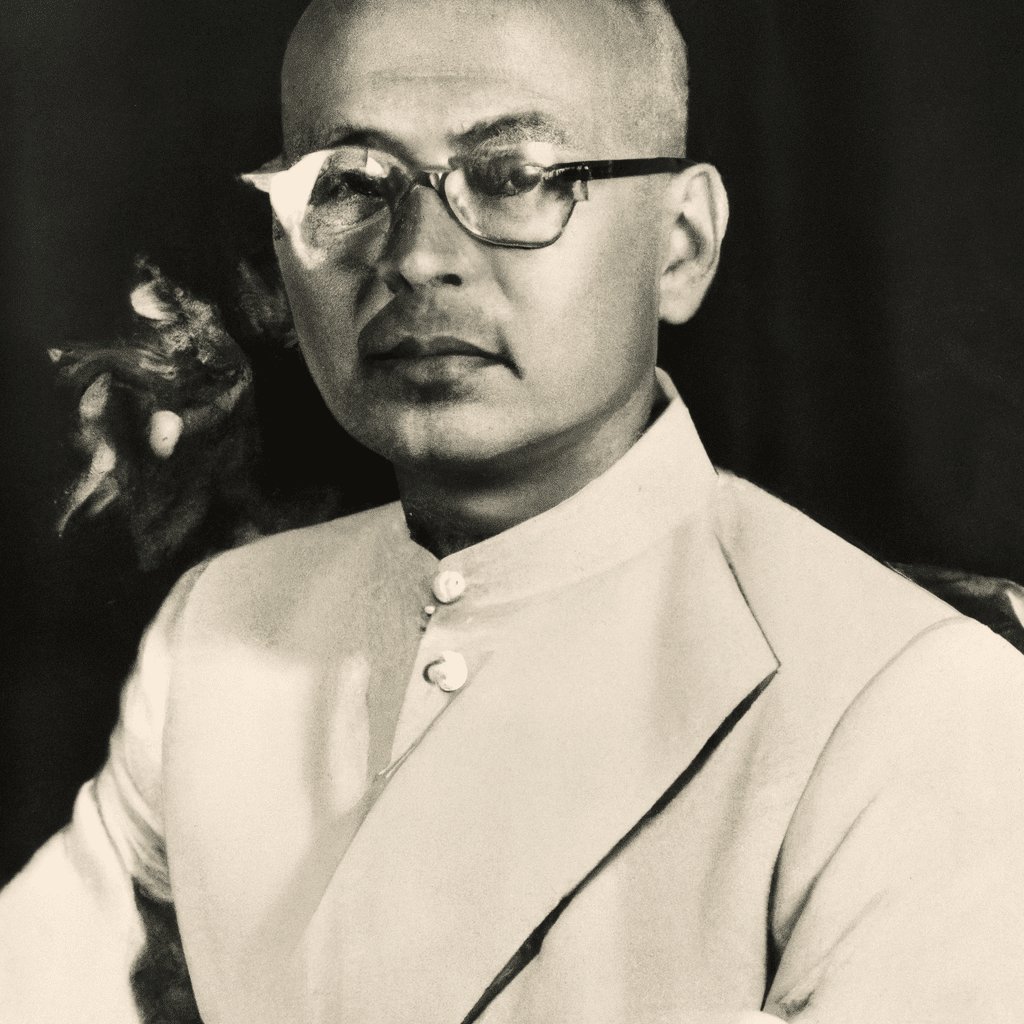
Manbendra Nath Roy (1887—1954)
Manbendra Nath Roy (1887—1954) M. N. Roy was a twentieth century Indian philosopher. He began his career as a militant political activist and left India in 1915 in search of arms for organizing an insurrection against…
Modal Metaphysics
Modal Metaphysics Modal metaphysics concerns the metaphysical underpinning of our modal statements. These are statements about what is possible or what is necessarily so. We can construe the primary question of modal metaphysics as, “When…
Maurice Blanchot (1907–2003)
Maurice Blanchot (1907–2003) Though Maurice Blanchot’s status as a major figure in 20th century French thought is indisputable, it is debatable how best to classify his thought and writings. To trace the itinerary of Blanchot’s…
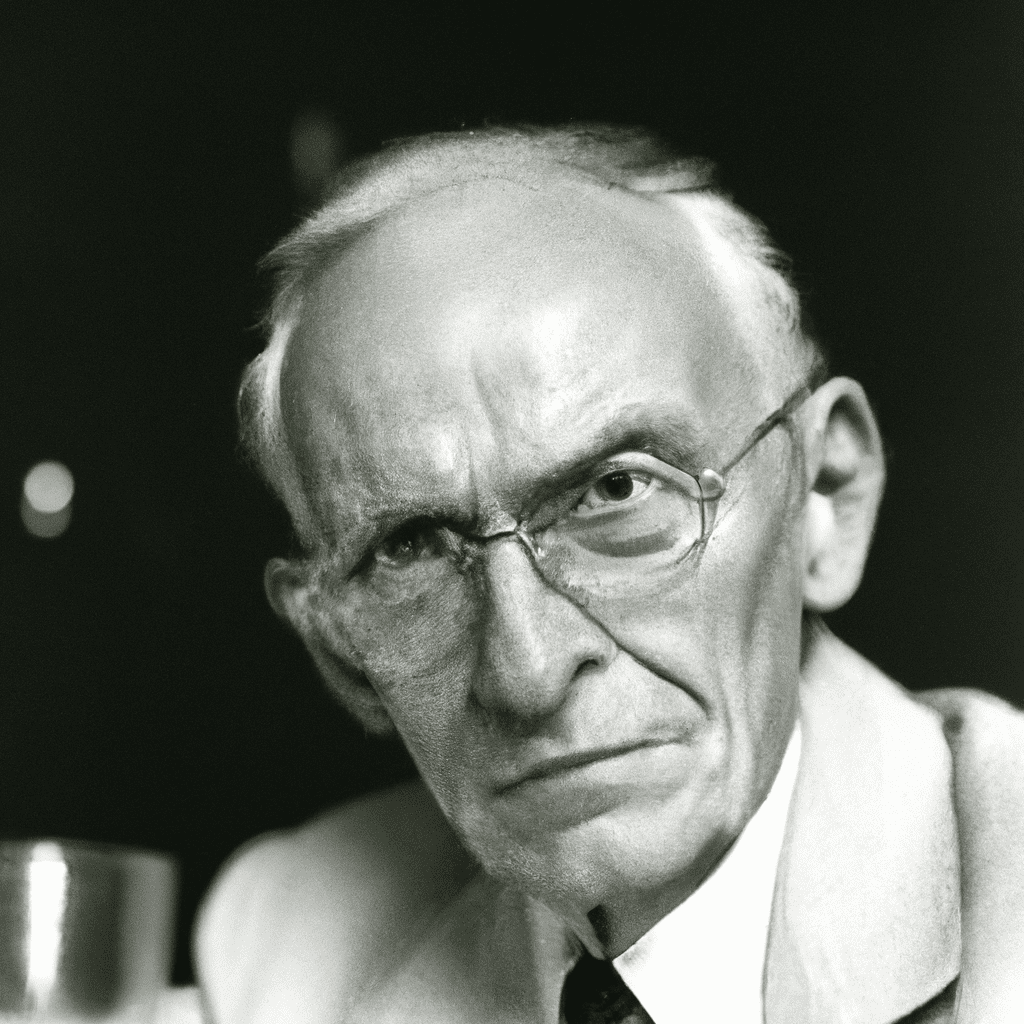
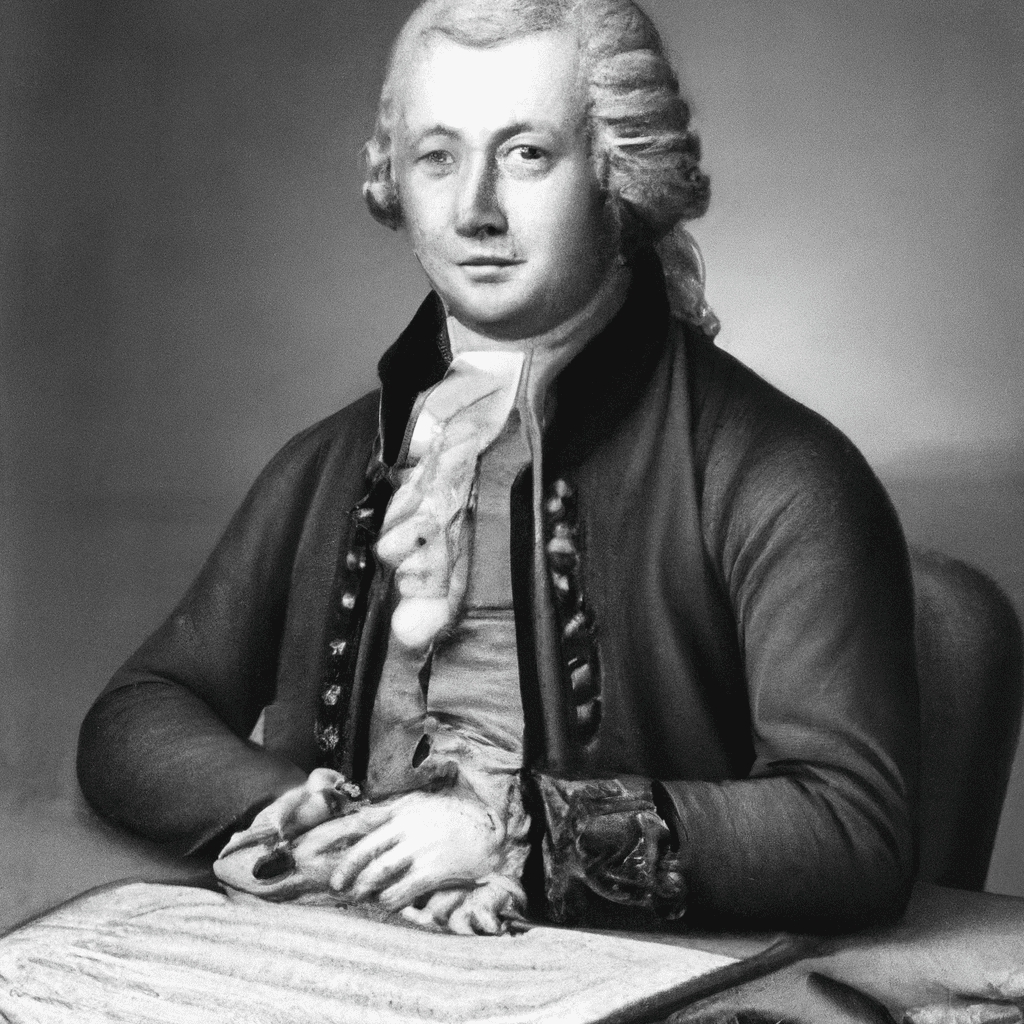
Johann Georg Hamann (1730—1788)
Johann Georg Hamann (1730—1788) Johann Georg Hamann was the philosophically most sophisticated thinker of the German Counter-enlightenment. Born in 1730 in Königsberg in eastern Prussia, Hamann was a contemporary and friendly acquaintance of the philosopher…
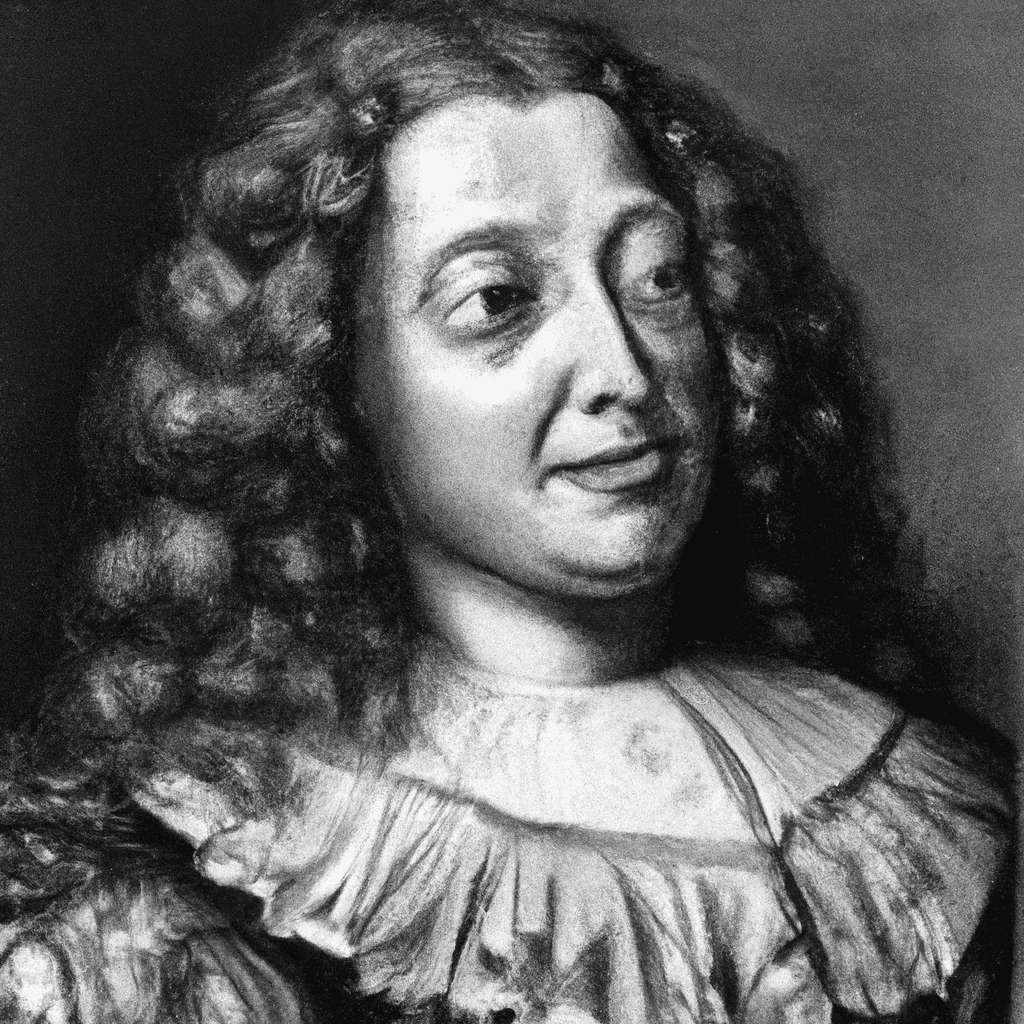
Jacqueline Pascal (1625—1661)
Jacqueline Pascal (1625—1661) A Cistercian nun, Jacqueline Pascal made a major contribution to philosophy of education through her treatise on the methods and principles of the pedagogy used at the convent school at Port-Royal. In…
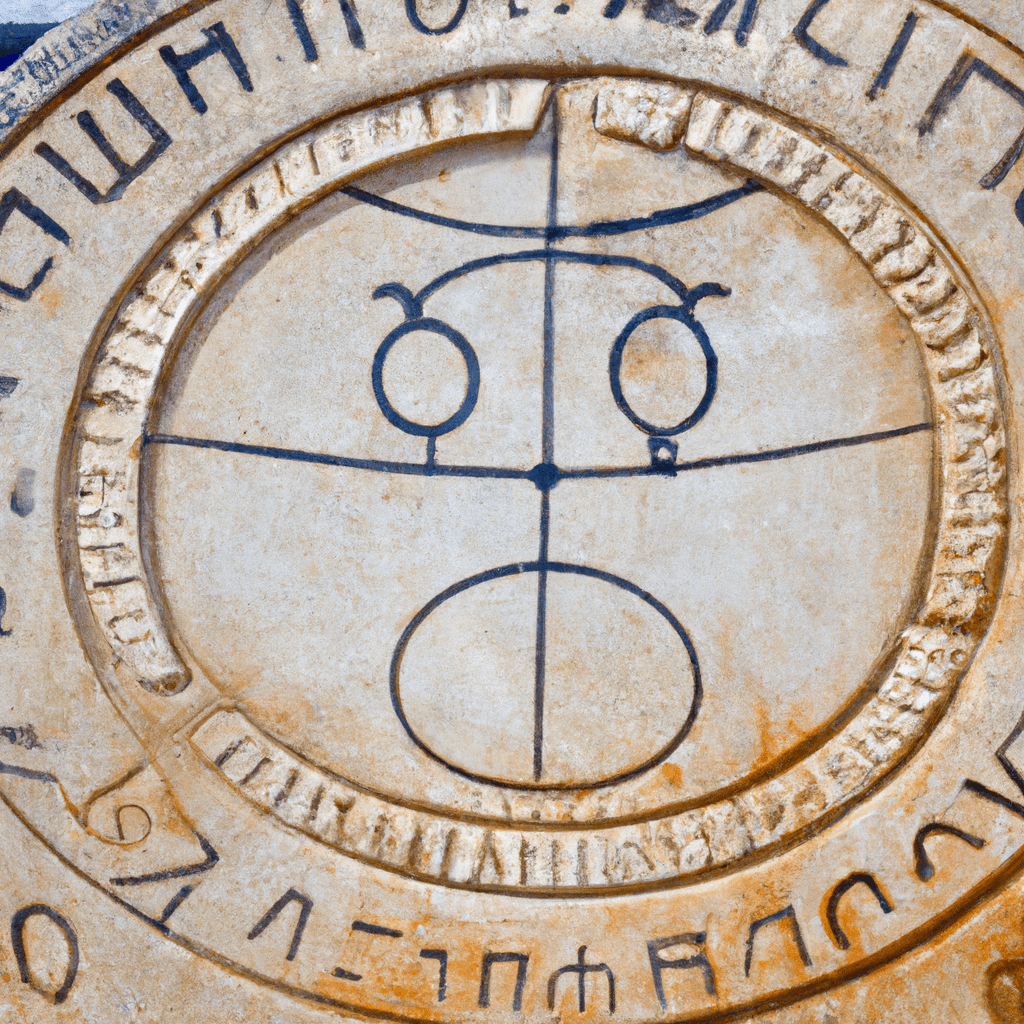
Hellenistic Astrology
Hellenistic Astrology Hellenistic and Late Antiquity astrologers built their craft upon Babylonian (and to a lesser extent Egyptian) astrological traditions, and developed their theoretical and technical doctrines using a combination of Stoic, Middle Platonic and…
Mulla Sadra (c. 1572—1640)
Mulla Sadra (c. 1572—1640) Mulla Sadra made major contributions to Islamic metaphysics and to Shi’i theology during the Safavid period (1501-1736) in Persia. He started his career in the context of a rising culture that…
Neo-Stoicism
Neo-Stoicism Neo-Stoicism (or Neostoicism) is the name given to a late Renaissance philosophical movement that attempted to revive ancient Stoicism in a form that would be acceptable to a Christian audience. This involved the rejection…