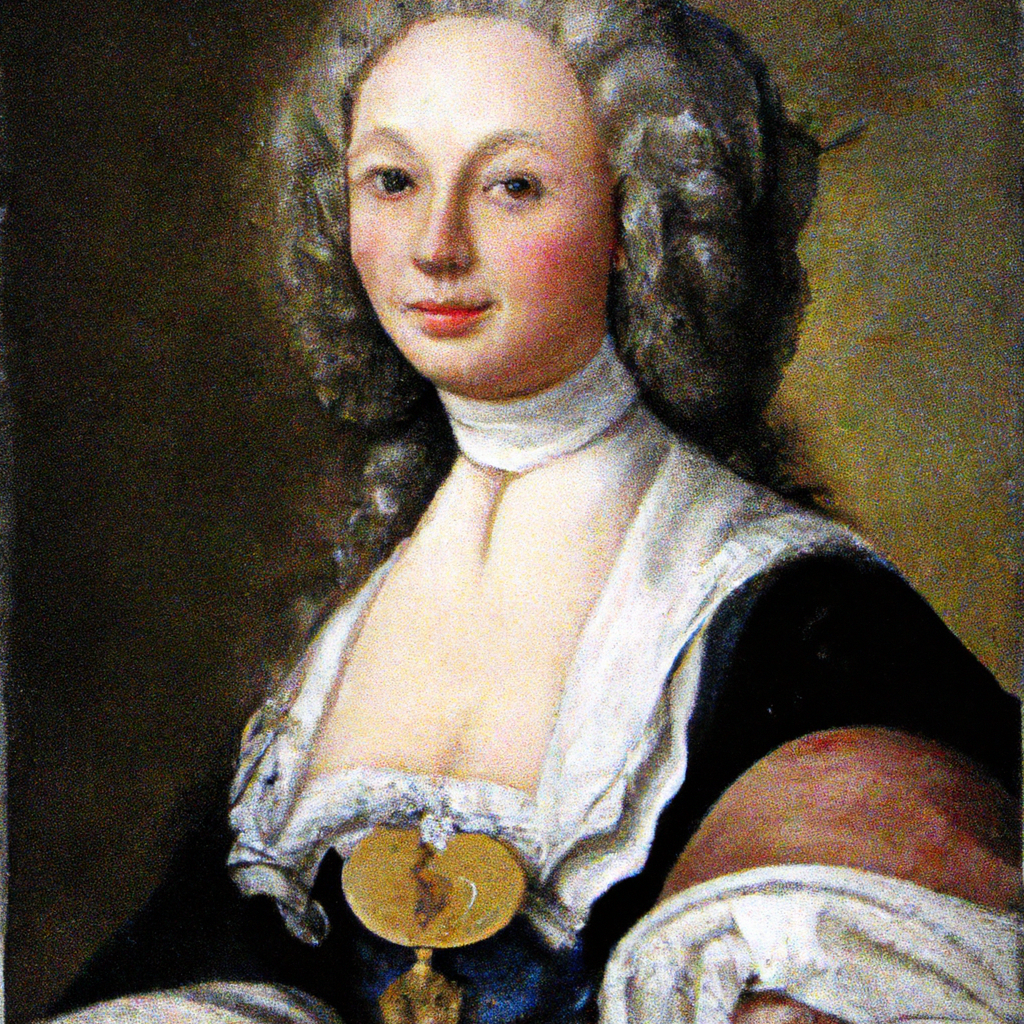
Angélique de Saint Jean Arnauld d’Andilly (1624–1684) Angélique de Saint-Jean Arnauld d’Andilly, an abbess of the convent of Port-Royal, was a leader of the intransigent party in the Jansenist movement. A prolific author, Mère Angélique…
Browsing CategoryWiki Filosofía
Empirical Aesthetics
Empirical Aesthetics Empirical aesthetics is a research area at the intersection of psychology and neuroscience that aims to understand how people experience, evaluate, and create objects aesthetically. Its central two questions are: How do we…
Locke: Epistemology
Locke: Epistemology John Locke (1632-1704), one of the founders of British Empiricism, is famous for insisting that all our ideas come from experience and for emphasizing the need for empirical evidence. He develops his empiricist…
Knowledge by Acquaintance and Knowledge by Description
Knowledge by Acquaintance and Knowledge by Description Our own experiences of pain are better known to us than the bio-chemical structure of our brains. Some philosophers hold that this difference is due to different kinds…
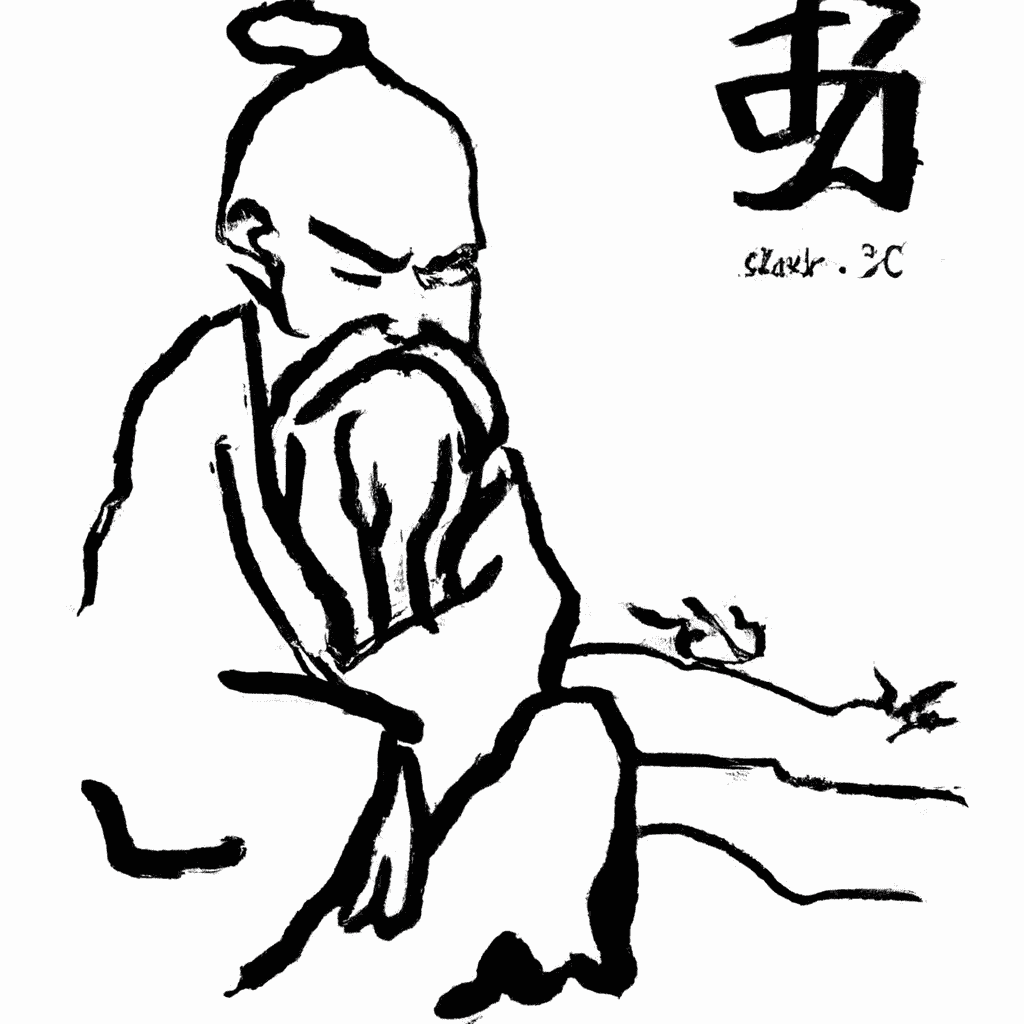
Laozi (Lao-tzu, fl. 6th cn. B.C.E.)
Laozi (Lao-tzu, fl. 6th cn. B.C.E.) Laozi is the name of a legendary Daoist philosopher, the alternate title of the early Chinese text better known in the West as the Daodejing, and the moniker of…
Natural Theology
Natural Theology Natural theology is a program of inquiry into the existence and attributes of God without referring or appealing to any divine revelation. In natural theology, one asks what the word “God” means, whether…
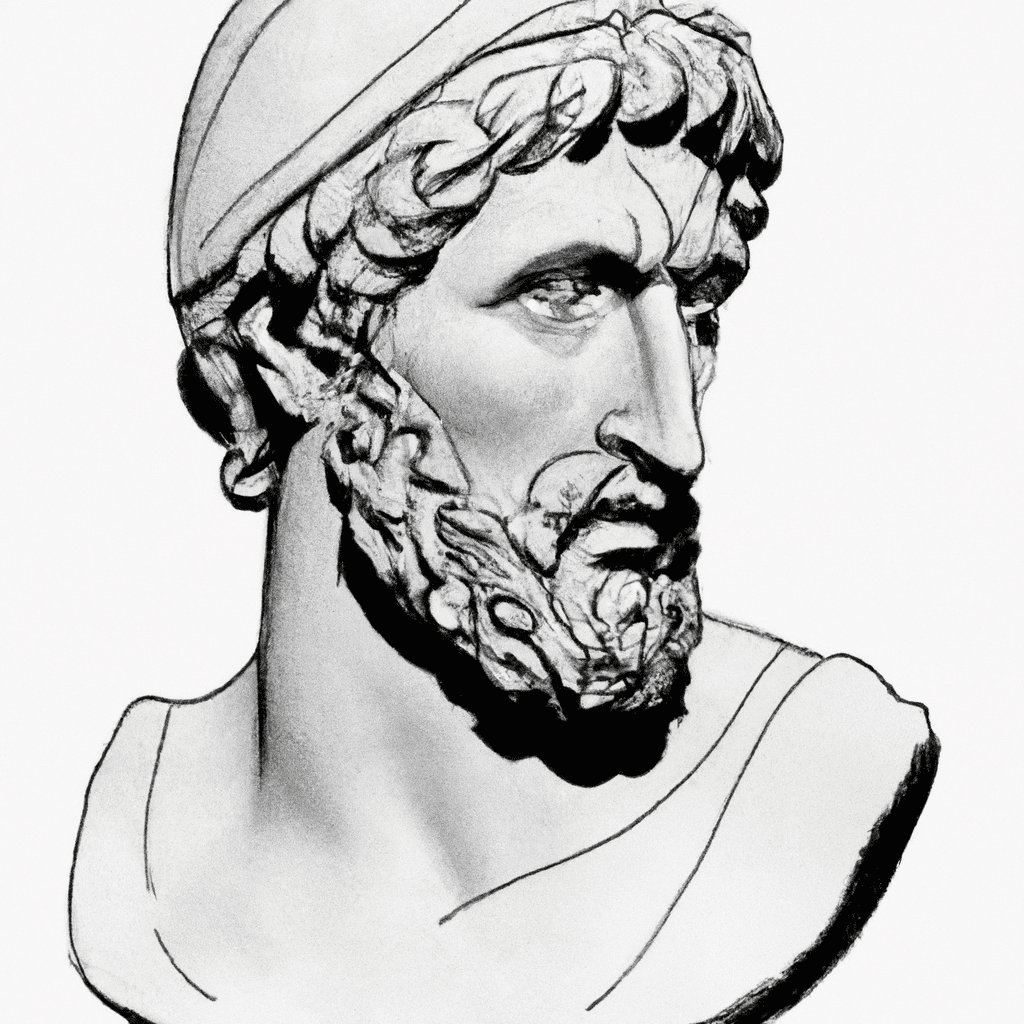
Thales of Miletus (c. 620 B.C.E.—c. 546 B.C.E.)
Thales of Miletus (c. 620 B.C.E.—c. 546 B.C.E.) The ancient Greek philosopher Thales was born in Miletus in Greek Ionia. Aristotle, the major source for Thales’s philosophy and science, identified Thales as the first person…
History of Love
History of Love What is love? We all wish to have the answer to one of the most universal, mysterious, and all-permeating phenomena on this planet. And even if we perhaps have a special feeling…
Political Constructivism
Political Constructivism Political Constructivism is a method for producing and defending principles of justice and legitimacy. It is most closely associated with John Rawls’ technique of subjecting our deliberations about justice to certain hypothetical constraints….