Aristoteles: Politics In his Nicomachean Ethics, Aristoteles (384-322 v. Chr.) describes the happy life intended for man by nature as one lived in accordance with virtue, und, in his Politics, he describes the role that politics and the political…
Browsing CategoryWiki-Philosophie
Socialism
Socialism Socialism is both an economic system and an ideology (in the non-pejorative sense of that term). A socialist economy features social rather than private ownership of the means of production. It also typically organizes…
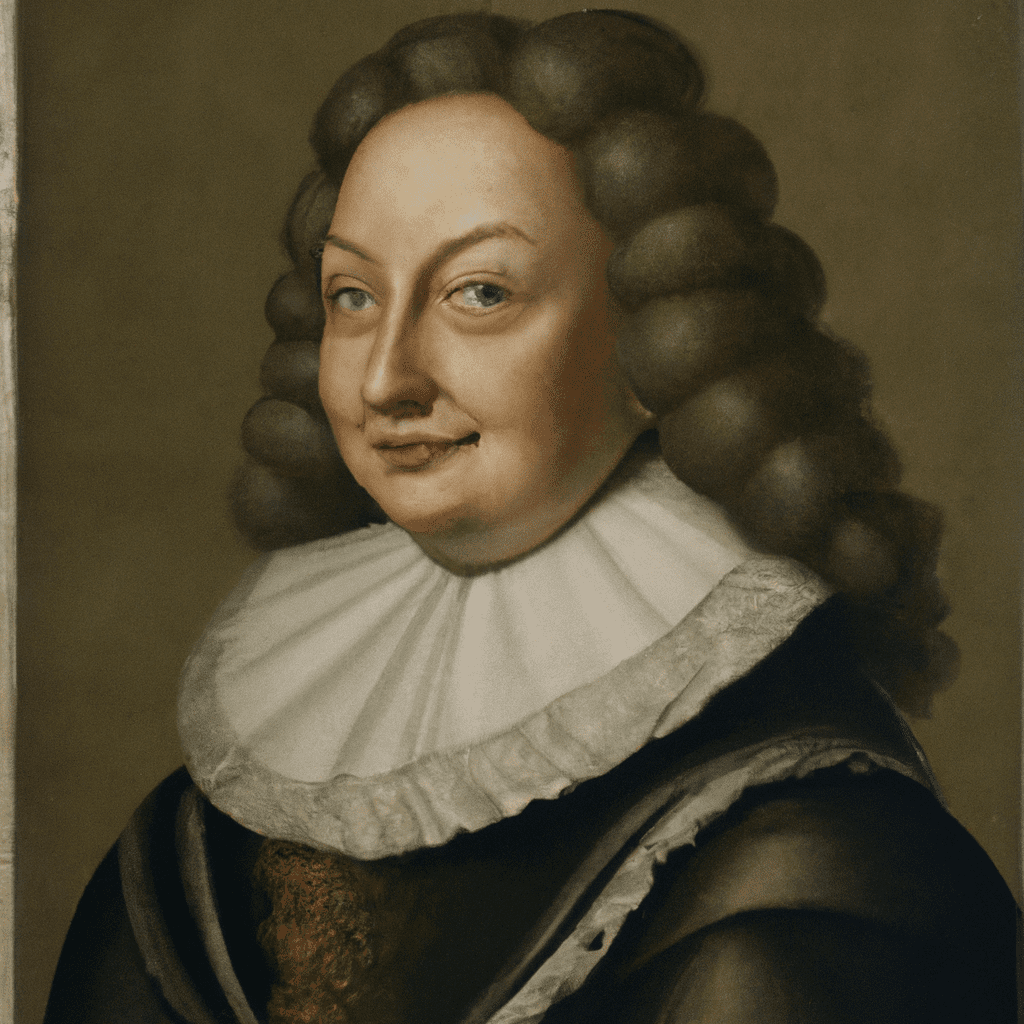
Angélique Arnauld (1591–1661)
Angélique Arnauld (1591–1661) Die reformierende Äbtissin des Klosters Port-Royal, Mère Angélique Arnauld entwickelte eine augustinische Philosophie, die stark von der Jansenistenbewegung beeinflusst war. Her philosophy of God follows the via negativa in its stress…
Neokolonialismus
Neokolonialismus Der Begriff „Neokolonialismus“ repräsentiert im Allgemeinen die Handlungen und Auswirkungen bestimmter Überbleibsel und Akteure der Kolonialzeit in einer bestimmten Gesellschaft. Postkoloniale Studien haben dies trotz der Erlangung der Unabhängigkeit ausführlich gezeigt, the influences…
Theory of Mind
Theory of Mind Theory of Mind is the branch of cognitive science that investigates how we ascribe mental states to other persons and how we use the states to explain and predict the actions of…
The Yablo Paradox
The Yablo Paradox The Yablo Paradox implies there is no way to coherently assign a truth value to any of the sentences in the countably infinite sequence of sentences, each of the form, “All of…
Constructive Mathematics
Constructive Mathematics Constructive mathematics is positively characterized by the requirement that proof be algorithmic. Grob gesagt, this means that when a (mathematical) object is asserted to exist, an explicit example is given: a constructive existence…
Ralph Waldo Emerson (1803—1882)
Ralph Waldo Emerson (1803—1882) In his lifetime, Ralph Waldo Emerson became the most widely known man of letters in America, establishing himself as a prolific poet, essayist, popular lecturer, and an advocate of social reforms…
Gottfried Leibniz: Metaphysik
Gottfried Leibniz: Metaphysics The German rationalist philosopher, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (1646-1716), is one of the great renaissance men of Western thought. He has made significant contributions in several fields spanning the intellectual landscape, including mathematics, Physik,…
The Evidential Problem of Evil
The Evidential Problem of Evil The evidential problem of evil is the problem of determining whether and, if so, to what extent the existence of evil (or certain instances, kinds, quantities, or distributions of evil)…